 |
|
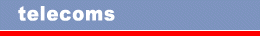
With the trend towards working from home, there is an increase
in communication equipment in the home such as telephones, fax
machines, computers and modems to access the internet.
Multi-function machines are now available which offer fax, copier,
printer, PC-fax, scanner and e-mail from one unit. |
|
|
Internet, Modem and Interactive
Services
A modem is a device which allows a computer or Digital Set Top Box
(STB) to send and receive information over a telephone line. It
can be an internal device built into the desktop, laptop, or STB,
a separate external box that connects to a computerís serial port,
or a PC card that plugs into the PC card slot found on most
laptops. |
|
|
|
|
Telephone
There are basically four types of telephone:
1. Analogue Corded The traditional telephone with a fixed
cord from the phone base to the handset.
2. Analogue Cordless The first system of cordless
technology with limited operating distances.
3. New Frequency Analogue Cordless
An enhanced system which uses eight channel technology, a new
frequency range of 31-39MHz and gives clearer call and larger
operating distance approx. 100m away from the base station.
4. DECT-Digital Enhanced Cordless Telephony
DECT phones that use digital cordless technology operate on 1.8GHz
and allow multiple handsets to be used from a single base station,
offering significantly greater range than analogue models,
improved reception and clearer speech.
Combined mobile/DECT cordless phones provide mobile and DECT
features in one smart handset, which can accept or make calls on
both mobile and land line networks. These use DECT protocol close
to the home and automatically switch to mobile use outside a
certain range.
Fax Machines
Fax machines plug into a telephone socket and have built-in
software to enable the user to transmit data for instance, a
letter, which can be received normally by another fax machine.
Early fax machines used thermal paper but more modern machines
print directly onto standard A4 paper.
|
|
|
Modems are available in a
variety of speeds. The faster the modem, the quicker the data can
be transferred and hence the shorter and cheaper the phone call
will be. This is provided the telephone line and other end of the
line can support the modem speed and protocol.
To connect a modem to a telephone line, the socket will need to be
a BT style socket. See following section on BT style sockets and
installing extensions. Faster access speeds are possible using
ISDN digital phone lines, or services such as BT Highway which
adds a digital line alongside your existing phone line. To connect
your computer to the digital line you need an ISDN adapter rather
than a modem, and the Internet Service Provider you choose must
offer ISDN support.
An alternative to the PC-modem-phone line or PC-ISDN approach is
to connect through the mobile phone networks, either by linking a
laptop to a mobile phone through a data card or an infra-red link.
Cable modems and STB modems are often used as the return path for
the interactive services offered by the terrestrial, satellite or
cable operators. These modems may also offer internet access via
the STB.

Telephone Extensions
Before installing a telephone extension, it is important to note
the Ring Equivalent Number (REN). Telephone lines have a REN of 4-
they can operate up to 4 telephone accessories (e.g. phones, fax,
answerphone), each with a REN of 1. |
|
| |
Next Page |
|
![]()